Primitives Reference: Difference between revisions
Holly-Wood (talk | contribs) No edit summary |
Holly-Wood (talk | contribs) No edit summary |
||
| Line 385: | Line 385: | ||
|- | |- | ||
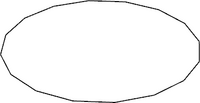
| [[File:4-4edge.png|200px|thumb|alt=4-4Edge]] | | [[File:4-4edge.png|200px|thumb|alt=4-4Edge]] | ||
|| This suite of primitives are used for edges which comprise an entire or part circle. | |||
''Currently available primitives:''<br> | ''Currently available primitives:''<br> | ||
Regular resolution (n-f) : 1-16, 1-8, 3-16, 1-4, 5-16, 3-8, 7-16, 2-4, 9-16, 5-8, 11-16, 3-4, 7-8, 4-4<br> | Regular resolution (n-f): 1-16, 1-8, 3-16, 1-4, 5-16, 3-8, 7-16, 2-4, 9-16, 5-8, 11-16, 3-4, 7-8, 4-4<br> | ||
High resolution (n-f) : 1-48, 1-24, 1-16, 1-12, 5-48, 1-8, 7-48, 1-6, 3-16, 5-24, 1-4, 7-24, 5-16, 1-3, 3-8, 19-48, 5-12, 7-16, 11-24, 2-4, 5-8, 2-3, 3-4, 4-4 | High resolution (n-f): 1-48, 1-24, 1-16, 1-12, 5-48, 1-8, 7-48, 1-6, 3-16, 5-24, 1-4, 7-24, 5-16, 1-3, 3-8, 19-48, 5-12, 7-16, 11-24, 2-4, 5-8, 2-3, 3-4, 4-4 | ||
|- | |||
| '''n-fdisc.dat''' || '''Circular disc sector''' | |||
|- | |||
| [[File:4-4disc.png|200px|thumb|alt=4-4disc]] | |||
|| This suite of primitives are used for surfaces which comprise an entire or part circle. | |||
''Currently available primitives:''<br> | |||
Regular resolution (n-f): 1-16, 1-8, 3-16, 1-4, 5-16, 3-8, 7-16, 2-4, 5-8, 3-4, 7-8, 4-4<br> | |||
High resolution (n-f): 1-12, 5-48, 1-8, 7-48, 1-6, 3-16, 1-4, 2-4, 4-4 | |||
|- | |||
| '''n-fndis.dat''' || '''Inverse of circular disc sector''' | |||
|- | |||
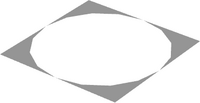
| [[File:4-4ndis.png|200px|thumb|alt=4-4ndisc]] | |||
|| This suite of primitives pad their matching n-fdisc.dat primitives out to the bounding square. They are used to integrate circular elements into rectilinear elements. | |||
''Currently available primitives:''<br> | |||
Regular resolution (n-f): 1-16, 1-8, 3-16, 1-4, 5-16, 3-8, 7-16, 2-4, 3-4, 7-8, 4-4<br> | |||
High resolution (n-f): 1-24, 1-16, 1-12, 5-48, 1-8, 7-48, 1-6, 3-16, 5-24, 1-4, 1-3, 2-4, 4-4 | |||
|- | |||
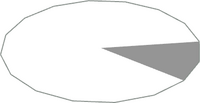
| '''n-fchrd.dat''' || '''Inverse of circular disc sector''' | |||
|- | |||
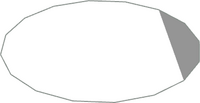
| [[File:1-4chrd.png|200px|thumb|alt=1-4chrd]] | |||
|| This suite of primitives are used for surfaces which comprise part of a circle enclosed by the arc of its circumference and its chord. Note that the bounding circle in the image is for context only - only the grey segment is generated by the 1-4chrd primitive. | |||
''Currently available primitives:''<br> | |||
Regular resolution (n-f): 1-16 (see note), 1-8, 3-16, 1-4, 5-16, 3-8, 7-16, 2-4, 5-8, 3-4, 13-16, 7-8<br> | |||
High resolution (n-f): 1-24, 1-16, 1-12, 1-8, 7-48, 1-6, 3-16, 5-24, 7-24, 1-3, 3-8, 19-48, 5-12, 1-4, 1-3 | |||
Note: The regular resolution 1-16chrd.dat is a special case, see Primitive Substitution Adapters below for more information | |||
|- | |||
| '''1-16chrd.dat'''<br>'''n-fering.dat''' || '''Primitive Substitution Adapters''' | |||
|- | |||
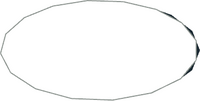
| [[File:4-4edge.png|200px|thumb|alt=4-4edge]] | |||
|| This suite of primitives are used correct for gaps that form between curved primitives and normal geometry in editors that utilize primitive substitution. This is a special case used on the inside of a curved primitive where it joins geometry that cannot make use of a curved primitive. The chrd files themselves are simply a reference to empty.dat, which under normal circumstances does not draw anything. However, in tools that support primitive substitution, the curved primitive it is attached to would normally in this case create a gap when rendered using more than 16 points to form a circle. In that case, the substituted version of these normally empty primitives would fill in the gap between the curve and the other geometry. | |||
To "see" these primitives, the editor in use must utilize primitive substitution. Then one of the following can be done: | |||
* set the curve quality to a level high enough to see the gaps reappear | |||
* For LDView 4.4 or later, in the Model Tree dialog, you can search for them (for example, "ering"), and if you have it set to highlight, then when you select one, it will be highlighted in the 3D view. | |||
* Manually recolor the primitive in question to a color that contrasts with the colors that surround it | |||
Note that the bounding circle in the image is for context only - there are no actual geometry producing lines contained in these files. | |||
''Currently available primitives:''<br> | |||
Regular resolution (n-f): 1-16chrd, 1-4ering, 1-8ering, 3-16ering, 2-4ering, 4-4ering<br> | |||
High resolution (n-f): none | |||
|- | |||
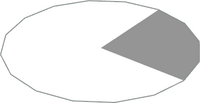
| '''n-ftang.dat''' || '''Tangential ring segment''' | |||
|- | |||
| [[File:1-4tang.png|200px|thumb|alt=1-4tang]] | |||
|| This suite of primitives are used to pad a 16-sided polygon to a circumscribing 16-sided polygon whose edges are tangential to the inner polygon. Note that the bounding circle in the image is for context only - only the grey segment is generated by the 1-4tang primitive. | |||
''Currently available primitives:''<br> | |||
Regular resolution (n-f): 1-8, 1-4 | |||
|- | |||
| '''n-fringr.dat'''<br>'''n-frinrr.dat'''<br>'''n-ffrinr.dat'''<br>'''n-ffrirr.dat'''<br>'''nn-ffrir.dat'''<br>ringr.dat (deprecated name)<br>ringrr.dat (deprecated name) || '''Circular ring segment''' | |||
|- | |||
| [[File:4-4ring1.png|200px|thumb|alt=1-4ring1]] | |||
|| This suite of primitives are used to generate circular rings or part rings. The numeric suffix r in the filename indicates the inner radius of the ring - the outer radius is 1LDu greater. For example a n-f4-4ring4 primitive would create a ring with an inner radius of 4LDu and an outer radius of 5LDu. | |||
''Currently available primitives:''<br> | |||
Regular resolution:<br> | |||
r=1 : 1-16rin1, 1-8ring1, 3-16rin1, 1-4ring1, 3-8ring1, 7-16rin1, 2-4ring1, 5-8ring1, 3-4ring1, 7-8ring1, 4-4ring1<br> | |||
r=2 : 1-16rin2, 1-8ring2, 3-16rin2, 1-4ring2, 5-16rin2, 3-8ring2, 7-16ring2, 2-4ring2, 5-8ring2, 3-4ring2, 7-8ring2, 4-4ring2<br> | |||
r=3 : 1-16rin3, 1-8ring3, 3-16rin3, 1-4ring3, 5-16rin3, 3-8ring3, 7-16rin3, 2-4ring3, 5-8ring3, 3-4ring3, 7-8ring3, 4-4ring3<br> | |||
r=4 : 1-16rin4, 1-8ring4, 3-16rin4, 1-4ring4, 3-8ring4, 7-16rin4, 2-4ring4, 5-8ring4, 3-4ring4, 4-4ring4<br> | |||
r=5 : 1-8ring5, 3-16rin5, 1-4ring5, 5-16rin5, 3-8ring5, 2-4ring5, 3-4ring5, 4-4ring5<br> | |||
r=6 : 1-8ring6, 3-16rin6, 1-4ring6, 3-8ring6, 2-4ring6, 5-8ring6, 3-4ring6, 4-4ring6<br> | |||
r=7 : 1-8ring7, 3-16rin7, 1-4ring7, 3-8ring7, 2-4ring7, 3-4ring7, 4-4ring7<br> | |||
r=8 : 1-8ring8, 3-16rin8, 1-4ring8, 3-8ring8, 2-4ring8, 3-4ring8, 7-8ring8, 4-4ring8<br> | |||
r=9 : 1-8ring9, 3-16rin9, 1-4ring9, 3-8ring9, 7-16ring9, 2-4ring9, 3-4ring9, 7-8ring9, 4-4ring9<br> | |||
r=10 : 1-8rin10, 1-4rin10, 3-8rin10, 2-4rin10, 5-8ring10, 3-4rin10, 4-4rin10<br> | |||
r=11 : 1-16ring11, 3-16ring11, 1-4rin11, 2-4rin11, 4-4rin11<br> | |||
r=12 : 1-8ring12, 3-16ring12, 1-4rin12, 5-16ring12, 3-8rin12, 2-4rin12, 7-8rin12, 4-4rin12<br> | |||
r=13 : 3-16ring13, 1-4rin13, 3-8rin13, 2-4rin13, 4-4rin13<br> | |||
r=14 : 3-16ring14, 1-4rin14, 2-4rin14, 3-4rin14, 4-4rin14<br> | |||
r=15 : 1-8rin15, 1-4rin15, 3-8rin15, 2-4rin15, 7-8rin15, 4-4rin15<br> | |||
r=16 : 1-4rin16, 3-8rin16, 2-4rin16, 7-8rin16, 4-4rin16<br> | |||
r=17 : 1-8rin17, 1-4rin17, 7-16ring17, 2-4rin17, 4-4rin17<br> | |||
r=18 : 1-8rin18, 1-4rin18, 3-8rin18, 2-4rin18, 4-4rin18<br> | |||
r=19 : 1-16ring19, 1-8rin19, 1-4rin19, 2-4ring19, 4-4rin19<br> | |||
r=20 : 1-4rin20, 4-4rin20<br> | |||
r=21 : 4-4rin21<br> | |||
r=22 : 2-4rin22, 3-4rin22, 4-4rin22<br> | |||
r=23 : 1-8rin23, 1-4rin23, 2-4rin23, 4-4rin23<br> | |||
r=24 : 3-16ring24, 1-4rin24, 3-8rin24, 2-4rin24, 4-4rin24<br> | |||
r=25 : 2-4rin25, 4-4rin25<br> | |||
r=26 : 4-4rin26<br> | |||
r=27 : 1-4ring27<br> | |||
r=28 : 1-4rin28<br> | |||
r=29 : 4-4rin29<br> | |||
r=30 : 2-4rin30, 4-4rin30<br> | |||
r=31 : 4-4rin31<br> | |||
r=32 : 4-4rin32<br> | |||
r=33 : 4-4rin33<br> | |||
r=34 : 1-4rin34, 4-4rin34<br> | |||
r=36 : 4-4rin36<br> | |||
r=37 : 2-4ring37, 4-4rin37<br> | |||
r=38 : 1-4rin38, 4-4rin38<br> | |||
r=39 : 1-8rin39, 1-4rin39, 7-8rin39, 4-4rin39<br> | |||
r=40 : 7-8rin40, 4-4rin40<br> | |||
r=43 : 2-4ring43, 4-4rin43<br> | |||
r=44 : 2-4ring44, 4-4rin44<br> | |||
r=45 : 4-4rin45<br> | |||
r=46 : 4-4rin46<br> | |||
r=47 : 4-4rin47<br> | |||
r=48 : 1-4rin48, 4-4rin48<br> | |||
r=49 : 1-4rin49<br> | |||
r=50 : 1-4rin50, 4-4rin50<br> | |||
r=51 : 4-4rin51<br> | |||
r=52 : 2-4rin52, 4-4rin52<br> | |||
r=57 : 4-4rin57<br> | |||
r=77 : 4-4rin77<br> | |||
r=78 : 4-4rin78<br> | |||
r=79 : 1-4ring79, 4-4rin79<br> | |||
r=85 : 4-4rin85<br> | |||
r=101 : 4-4ring101<br> | |||
<br> | |||
High resolution:<br> | |||
r=1 : 1-12rin1, 1-8ring1, 1-6ring1, 1-4ring1, 2-4ring1<br> | |||
r=2 : 1-12rin2, 1-8ring2, 1-4ring2, 1-3ring2, 2-4ring2, 4-4ring2<br> | |||
r=3 : 1-24rin3, 1-16rin3, 1-12ring3, 1-8ring3, 1-6ring3, 1-4ring3, 7-16rin3, 2-4ring3, 4-4ring3<br> | |||
r=4 : 1-24rin4, 1-12ring4, 5-48rin4, 1-8ring4, 1-4ring4, 7-24rin4, 2-4ring4, 4-4ring4<br> | |||
r=5 : 1-24rin5, 1-12rin5, 5-48rin5, 1-8ring5, 7-48rin5, 1-6ring5, 5-24ring5, 1-4ring5, 2-4ring5, 4-4ring5<br> | |||
r=6 : 1-48rin6, 1-24rin6, 1-12rin6, 1-8ring6, 5-24ring6, 2-4ring6, 5-6ring6, 4-4ring6<br> | |||
r=7 : 1-24rin7, 1-8ring7, 1-6ring7, 3-16rin7, 5-24rin7, 2-3ring7, 3-4ring7, 4-4ring7<br> | |||
r=8 : 1-16rin8, 1-12rin8, 1-8ring8, 1-6ring8, 3-16rin8, 1-4ring8, 4-4ring8<br> | |||
r=9 : 1-48rin9, 1-24rin9, 1-12rin9, 5-48rin9, 1-8ring9, 5-24rin9, 1-6ring9, 1-4ring9, 1-3ring9, 2-4ring9, 4-4ring9<br> | |||
r=10 : 7-48ring10, 1-4rin10, 5-24ring10, 4-4rin10<br> | |||
r=11 : 1-24ring11, 1-4rin11, 2-4rin11, 4-4rin11<br> | |||
r=12 : 1-12ring12, 1-4ring12, 1-6rin12, 2-4rin12, 4-4rin12<br> | |||
r=13 : 1-16ring13, 1-6rin13, 5-24ring13, 1-4rin13, 5-12ring13, 11-24ring13, 3-4rin13, 4-4rin13<br> | |||
r=14 : 1-16ring14, 1-8rin14, 1-6rin14, 5-12ring14, 3-4rin14, 4-4rin14<br> | |||
r=15 : 1-12ring15, 1-4rin15, 4-4rin15<br> | |||
r=16 : 1-8rin16, 1-6rin16, 1-4rin16, 7-16ring16, 2-4rin16, 3-4rin16, 5-6rin16, 4-4rin16<br> | |||
r=17 : 1-12ring17, 1-6rin17, 5-24ring17, 1-4rin17, 1-3rin17, 2-4rin17, 4-4rin17<br> | |||
r=18 : 1-6rin18, 5-24ring18, 4-4rin18<br> | |||
r=19 : 1-24ring19, 1-16ring19, 1-6rin19, 11-48ring19, 1-4rin19, 2-4rin19, 4-4rin19<br> | |||
r=20 : 1-12ring20, 1-8rin20, 5-24ring20, 1-4rin20, 4-4rin20<br> | |||
r=21 : 1-16ring21, 1-4rin21, 4-4rin21<br> | |||
r=22 : 1-4rin22, 4-4rin22<br> | |||
r=23 : 1-4rin23<br> | |||
r=24 : 5-24ring24, 1-4rin24, 4-4rin24<br> | |||
r=25 : 1-4rin25, 4-4rin25<br> | |||
r=26 : 1-4rin26, 4-4rin26<br> | |||
r=27 : 1-4rin27, 4-4rin27<br> | |||
r=28 : 1-8rin28, 5-24ring28, 4-4rin28<br> | |||
r=29 : 1-24ring29, 1-16ring29, 1-12ring29, 1-6ring29, 1-4rin29, 5-24ring29, 4-4rin29<br> | |||
r=30 : 1-4rin30, 4-4rin30<br> | |||
r=31 : 1-4rin31, 2-4rin31<br> | |||
r=32 : 1-4rin32, 5-48ring32<br> | |||
r=33 : 1-4rin33, 4-4rin33<br> | |||
r=34 : 1-4rin34, 4-4rin34<br> | |||
r=35 : 1-8rin35, 5-24ring35, 1-4rin35, 4-4ring35<br> | |||
r=36 : 1-4rin36<br> | |||
r=37 : 1-4rin37, 2-4ring37, 4-4rin37<br> | |||
r=38 : 1-12ring38<br> | |||
r=39 : 1-24ring39, 1-12ring39, 1-8rin39, 1-6ring39, 3-16ring39, 1-4rin39, 4-4ring39<br> | |||
r=40 : 1-4rin40, 11-48ring40, 2-4ring40<br> | |||
r=41 : 1-4rin41, 4-4rin41<br> | |||
r=42 : 1-12ring42, 1-6ring42, 4-4rin42<br> | |||
r=43 : 1-48ring43, 1-16ring43, 1-6ring43, 4-4ring43<br> | |||
r=44 : 4-4ring44<br> | |||
r=45 : 1-4rin45<br> | |||
r=47 : 1-6rin47, 4-4rin47<br> | |||
r=48 : 1-4rin48<br> | |||
r=49 : 4-4rin49<br> | |||
r=50 : 1-6rin50, 4-4rin50<br> | |||
r=51 : 1-4rin51<br> | |||
r=52 : 11-24ring52, 4-4rin52<br> | |||
r=53 : 4-4rin53<br> | |||
r=54 : 4-4rin54<br> | |||
r=56 : 1-8rin56<br> | |||
r=60 : 1-24ring60, 1-16ring60<br> | |||
r=63 : 1-4rin63<br> | |||
r=64 : 1-4rin64<br> | |||
r=65 : 1-4rin65<br> | |||
r=70 : 1-4rin70<br> | |||
r=71 : 1-4rin71, 4-4ring71<br> | |||
r=78 : 1-12ring78<br> | |||
r=80 : 7-48ring80, 1-6ring80<br> | |||
r=82 : 1-4rin82<br> | |||
r=83 : 1-4rin83<br> | |||
r=97 : 4-4rin97<br> | |||
r=99 : 1-6ring99, 4-4ring99<br> | |||
r=100 : 4-4ring100<br> | |||
r=179 : 1-4ring179<br> | |||
r=240 : 2-4ring240<br> | |||
|} | |} | ||
Revision as of 06:40, 30 November 2023
LDraw Primitives Reference
This page is a source of reference for the LDraw primitives in the \LDraw\p directory. Primitives are defined as highly re-usable components of LEGO parts modelled for LDraw. They serve several purposes :
* To speed up parts authoring by providing a library of components which can be incorporated into several parts * To allow rendering software to make substitutions of curved components
Within this reference material the available primitives are categorised into:
Each section contains an overview of the characteristics common to all primitives within that category. Primitives are grouped into classes within each category - one class of primitive serving a similar purpose at different sizes or resolutions. For each class of primitive, a brief description of the purpose of the primitive is provided, with notes on its co-ordinate origin, default size and rules for scaling. A list of the available primitives is shown.
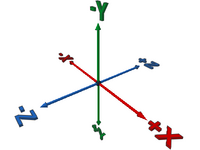
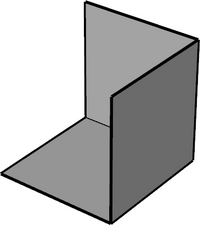
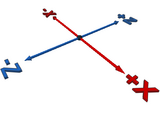
An understanding of the orientation of the co-ordinate axes is essential for authoring a part for LDraw. For reference within this page the axes and their direction is shown in this diagram.
Rectilinear primitives
These rectilinear elements may be scaled in the {x}, {y} and {z} dimensions to make elements of any size. For example
1 16 0 0 0 40 0 0 0 1 0 0 0 20 rect.dat
would generate a 80LDu x 40LDu rectangle in the {x,z} plane.
Although the default orientation of the rect.dat primitive is in the {x,z} plane the LDraw language allows for this to be transformed
1 16 0 0 0 0 1 0 40 0 0 0 0 20 rect.dat
would generate a 80LDu x 40LDu rectangle in the {y,z} plane.
1 16 0 0 0 40 0 0 0 0 20 0 1 0 rect.dat
would generate a 80LDu x 40LDu rectangle in the {x,y} plane.
Curved primitives
LDraw represents curved surfaces as polygons. For circular components two series of primitives are provided.
All the circular primitives are orientated in the {x,z} plane with their origin at the centre of the circle and a default radius of 1 LDu. Primitives are provided for complete circles and for commonly used fractions of a complete circle. Where the naming convention includes a prefix of the form n-f this indicates the fraction (n/f) of the circle drawn by the primitive. Where this fraction is less than an entire circle, the primitive starts at {+x,0} and progresses in a conterclockwise direction when viewed from above {-y}.
To avoid rounding errors, it is preferable to use existing fractional circular primitives, or create a new primitive, rather than rotate an existing primitive by anything other than 90 or 180 degrees. For example, use 3-16XXXX.dat rather than combining 1-8XXXX.dat with 1-16XXXX.dat rotated by 22.5 degreees.
To avoid matrix arithmetic problems in some renderers, the third dimension ({y} in the default orientation) of two-dimensional primitives must be given a non-zero scaling factor. LDraw circles are normally formed of 16-sided polygons (hexdecagons) - the regular resolution. For larger elements, where scaling-up of hexadecagons would give too angular an appearance, a series of high resolution primitives based on a 48-sided polygon are available. These may also be used for parts not well suited to a 16-fold symmetry.
These circular elements may be scaled by the same factor in both the {x} and {z} dimensions to make circular elements of greater or less than 1LDu radius. For example
1 16 0 0 0 3 0 0 0 1 0 0 0 3 4-4edge.dat
would generate a circle in the {x,z} plane with a radius of 3LDu.
They may also be scaled asymmetrically in the x and z dimension to make ellipses.
Although the default orientation is in the {x,z} plane the LDraw language allows for these to be transformed
1 16 0 0 0 0 1 0 3 0 0 0 0 3 4-4edge.dat would generate a circle in the {y,z} plane
1 16 0 0 0 3 0 0 0 0 3 0 1 0 4-4edge.dat would generate a circle in the {x,y} plane